Breakout trading is a popular strategy used by traders in the financial markets to capitalize on significant price movements. It involves identifying key levels of support and resistance and taking advantage of breakouts, where the price breaks through these levels, indicating a potential trend reversal or a continuation of an existing trend. In this article, we will delve into the world of breakout trading, exploring various breakout patterns and essential strategies that can help you make informed trading decisions.
1. Introduction to Breakout Trading
Breakout trading is based on the simple yet powerful principle of buying an asset when its price breaks above a critical resistance level or selling when it breaks below a key support level. The strategy aims to enter trades at the early stages of a new trend, allowing traders to ride the price momentum and potentially maximize profits.
2. Understanding Breakouts and Their Importance
Breakouts are pivotal points in the market, indicating shifts in supply and demand dynamics. When an asset’s price breaks through a significant level of support or resistance, it suggests a potential change in market sentiment. Identifying breakouts timely can provide traders with valuable entry opportunities.
3. Identifying Breakout Patterns
3.1. Symmetrical Triangles
Symmetrical triangles are characterized by converging trendlines that connect a series of lower highs and higher lows. Traders often anticipate a breakout as the price nears the triangle’s apex.
3.2. Ascending Triangles
Ascending triangles have a horizontal top trendline and an upward-sloping bottom trendline. This pattern indicates potential bullish breakouts.
3.3. Descending Triangles
Descending triangles feature a horizontal bottom trendline and a downward-sloping top trendline. This pattern suggests potential bearish breakouts.
3.4. Rectangles
Rectangles have horizontal support and resistance levels, with the price oscillating between them until a breakout occurs.
3.5. Flags and Pennants
Flags and pennants are small congestion patterns that can signal a continuation of the existing trend after a brief consolidation.
3.6. Head and Shoulders
Head and Shoulders is a classic reversal pattern, consisting of three peaks, with the middle peak (head) being higher than the other two (shoulders).
4. Key Breakout Trading Strategies
4.1. Momentum Trading
Momentum trading involves entering positions when an asset’s price exhibits strong upward momentum. Traders look for breakouts with high trading volumes to confirm the strength of the new trend.
4.2. Retracement Trading
Retracement trading involves waiting for a breakout and then entering the trade during price retracements. Traders aim to enter at a favorable price point within the new trend.
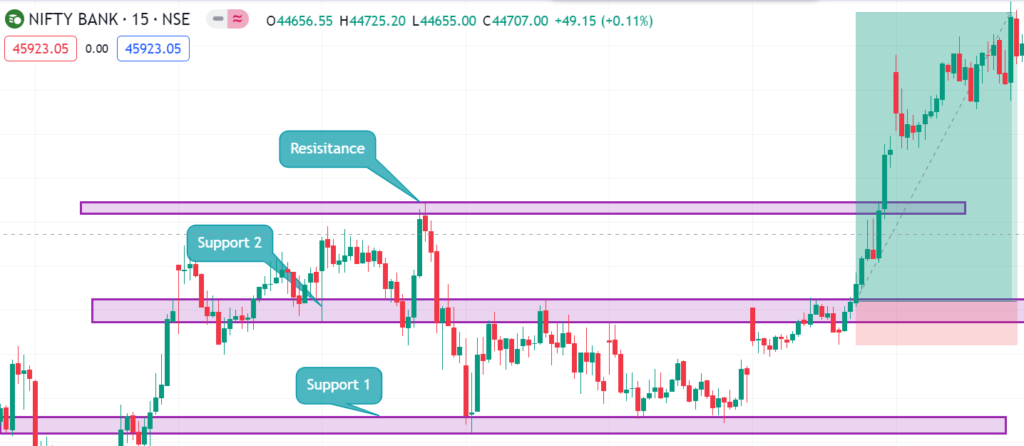
4.3. Support and Resistance Levels
Identifying reliable support and resistance levels is crucial for breakout traders to make informed decisions.
4.4. Moving Averages
Moving averages can help traders identify trends and potential breakout points more effectively.
4.5. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands provide valuable information about price volatility and potential breakout opportunities.
5. Implementing Breakout Trading
5.1. Setting Clear Entry and Exit Points
Establishing precise entry and exit points is essential for managing risk and optimizing profits.
5.2. Risk Management
Implementing a sound risk management strategy is crucial for preserving capital in volatile markets.
5.3. Using Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders can protect traders from significant losses in case the breakout does not materialize as expected.
6. Tips for Successful Breakout Trading
6.1. Stay Updated with Market News
Being informed about market developments and news can help traders anticipate potential breakouts.
6.2. Avoid Overtrading
Overtrading can lead to hasty decisions and increased exposure to risk. Stick to your trading plan.
6.3. Stick to Your Strategy
Consistency is key in breakout trading. Avoid switching strategies too frequently.
6.4. Learn from Failures
Breakout trading involves risks, and not all trades will be successful. Learn from your failures to improve future outcomes.
7. Advantages and Risks of Breakout Trading
7.1. Advantages
Breakout trading can yield substantial profits, especially during significant market movements.
7.2. Risks
False breakouts and whipsaws can lead to losses, especially in choppy or sideways markets.
8. Breakout Trading Examples

8.1. Example 1: Symmetrical Triangle Breakout
Illustrative example of how to identify and trade a symmetrical triangle breakout.
8.2. Example 2: Head and Shoulders Breakout
Real-world example of a head and shoulders pattern and how to execute the breakout trade.
9. Conclusion
Breakout trading is a dynamic strategy that enables traders to capitalize on price movements with substantial profit potential. By understanding various breakout patterns and employing effective trading strategies, traders can navigate the markets with confidence. However, it is essential to remain disciplined, manage risks, and continually improve one’s trading skills.
5 Unique FAQs
1.Q: How do I know if a breakout is genuine or a false signal?
A: Confirming breakouts with high trading volumes and strong price momentum can help distinguish genuine breakouts from false ones.
2.Q: Can breakout trading be applied to all financial markets?
A: Yes, breakout trading principles can be applied to stocks, forex, commodities, and other financial markets.
3.Q: What is the typical duration of a breakout trade?
A: The duration of a breakout trade can vary, ranging from a few hours to several weeks, depending on the timeframe and the asset being traded.
4.Q: Is breakout trading suitable for beginners?
A: Breakout trading requires some understanding of technical analysis and risk management, making it more suitable for intermediate to advanced traders.
5.Q: How can I stay disciplined in my breakout trading approach?
A: Creating a detailed trading plan, setting clear goals, and following strict risk management rules can help maintain discipline in breakout trading.

Thhis is a Fabulous content for both newbies
aand sesoned traders.
Feel free to surf to my web page: QuantStrategy